Is DC variable frequency heat pump suitable for every family?
As global energy costs rise and sustainability becomes a priority, DC inverter heat pumps are gaining traction as a cutting-edge solution for home heating and cooling. However, a critical question remains: Are these advanced systems truly suitable for every household? This article breaks down the technology’s pros, limitations, and ideal use cases to help homeowners make informed decisions.
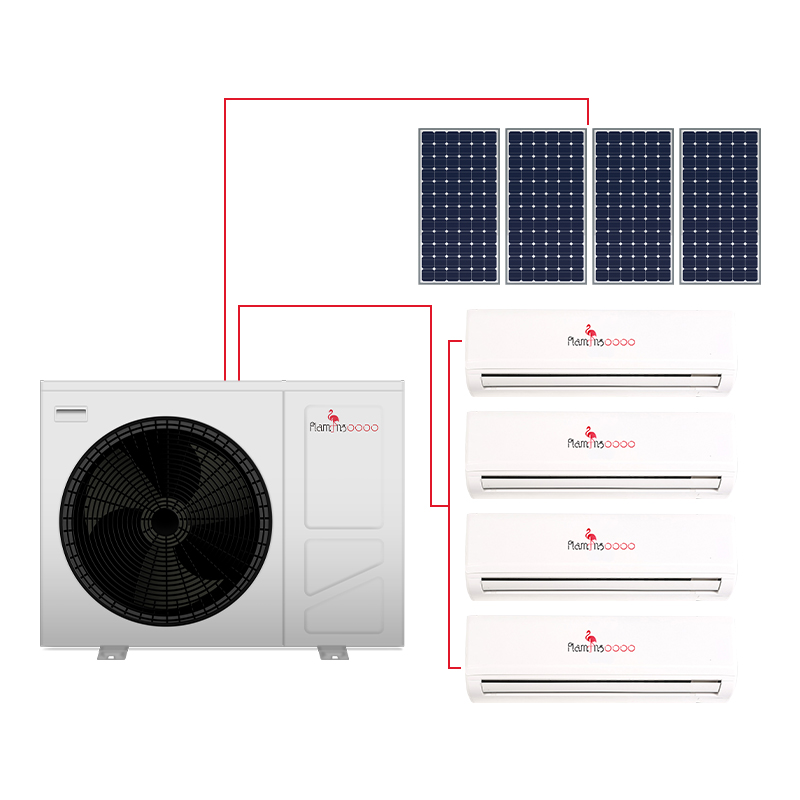
Why DC Inverter Heat Pumps Stand Out
DC inverter heat pumps use variable-speed compressors to adjust energy output dynamically, offering distinct advantages over traditional HVAC systems:
Energy Efficiency & Cost Savings:By minimizing frequent start-stop cycles, these systems reduce energy waste, achieving 30% higher COP (Coefficient ofPerformance) than fixed-speed models. Long-term savings on electricity bills make them a cost-effective choice.
Precision Temperature Contro:Maintain indoor temperatures within ±0.5°C fluctuations, ideal for households with infants, elderly members, or health-sensitive individuals.
Quiet Operation: Noise levels drop to 20 dB during low-speed operation, ensuring uninterrupted sleep and minimal disturbance.
Eco-Friendly Design: Many models use low-GWP (Global Warming Potential) refrigerants, aligning with global carbon reduction goals.
Who Should Consider a DC Inverter Heat Pump?
While highly efficient, DC inverter heat pumps are not universally ideal. Key scenarios where they excel include:
High-Usage Households: Families in regions with long heating/cooling seasons (e.g., cold winters or hot summers) benefit most from energy savings.
Comfort-Focused Homes: Perfect for those prioritizing stable indoor climates, such as homes with newborns, allergy sufferers, or smart-home integration.
Climate-Compatible Areas: Systems perform optimally in regions where winter temperatures stay above -25°C (unless equipped with enhanced low-temperature operation).
Potential Limitations to Evaluate
Upfront Costs: DC inverter models have higher initial prices than traditional units. Short-term residents (e.g., renters) may not recoup the investment quickly.
Extreme Cold Challenges: In areas below -30°C, standard models may require supplemental heating (e.g., electric auxiliaries).
Infrastructure Readiness: Homes with outdated electrical systems might need circuit upgrades to support the heat pump’s power demands.
Expert Tips for Choosing the Right System
Assess Needs: Prioritize either long-term savings or immediate budget constraints. Calculate payback periods based on local energy prices.
Professional Inspection: Have technicians evaluate your home’s insulation quality, electrical capacity, and installation space for outdoor units.
Compare Certified Models: Look for ENERGY STAR® or EU CE certifications and prioritize features like low-temperature performance and noise ratings.
DC inverter heat pumps represent a leap forward in energy-efficient HVAC, but their suitability hinges on individual circumstances. For eco-conscious homeowners in moderate climates, they deliver unmatched savings and comfort. However, those in extreme environments or temporary housing might explore hybrid systems or conventional alternatives.